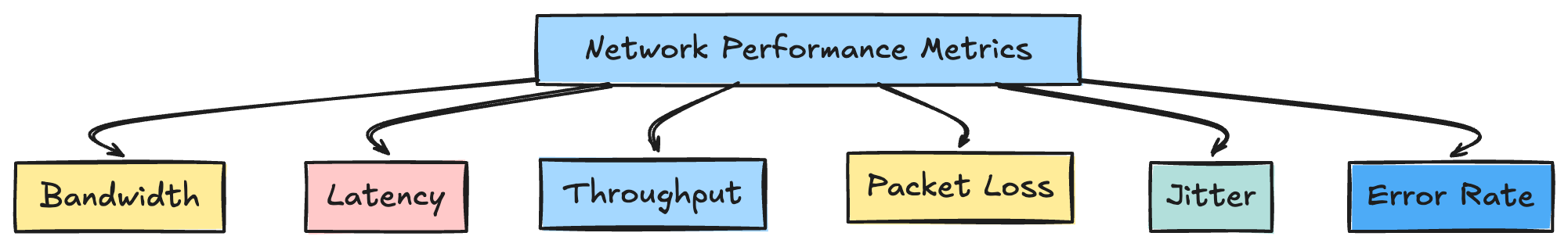
Network performance metrics are important in maintaining network infrastructure
Network performance metrics provide information regarding the health and security of a network and highlight areas that require optimization
Here are some of the Key Network Performance metrics:
- Bandwidth
- Latency
- Throughput
- Packet Loss
- Jitter
- Error Rate
- Quality of Service Metrics (QoS)
- Network Utilization
- Security and Performance integration
1. Bandwidth
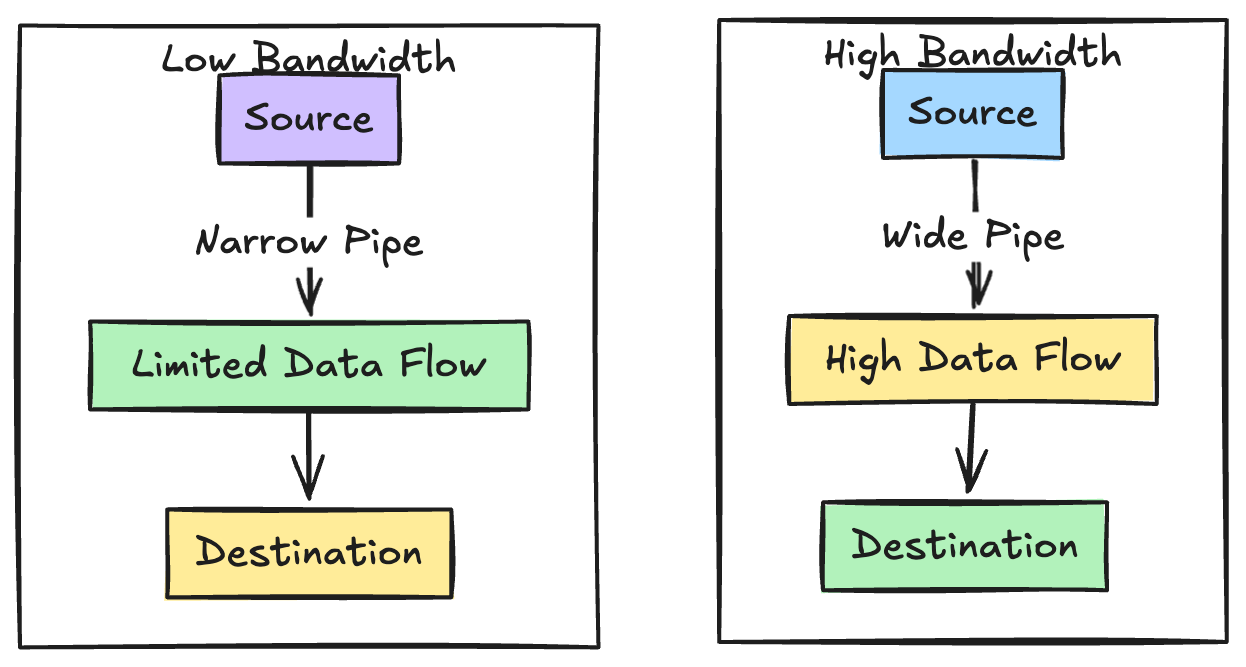
Bandwidth is the maximum rate at which data can be transferred over a network under ideal conditions, this is measured in Mbps or Mega bits per second
It is the data carrying capacity of a network connection, that is the maximum data a network connection can carry.
Why is bandwidth important?
Bandwidth means how much data can be transmitted in a specified amount of time
Higher bandwidth means more data can flow in a specified amount of time. Which means you can do activities like stream high quality videos, transfer large files faster, and supporting multiple users simultaneously
Factors affecting Bandwidth:
- Network Hardware: The network hardware needs to be good in order to support higher bandwidth, the quality of routers, switches and networking hardware needs to be latest
- Network Configuration: The network configuration also needs to be optimal otherwise you will not get the optimal bandwidth utilization out of the network. Improper settings can hamper otherwise good hardware and connectivity.
- Network Traffic: The amount of traffic that is already in the network and the type of traffic that is on the network affects the bandwidth
Optimization Strategies
- Upgrading Hardware: Replace the old equipment with high capacity devices that can handle high bandwidth
- Optimizing Configurations: Adjust network settings to prioritize important applications and use-cases
- Removing Unnecessary Traffic: Implement network policies to reduce the use of unnecessary data like unnecessary backups and things like that
- Implementing QoS Policies: Using the Quality of Service to prioritize things like user web browsing or streaming and doing backups and such at a lower priority helps improve experience of users as well as optimizes the bandwidth utilization
2 Latency
Latency is the time taken by a data packet to travel from its source to the destination in a given network. It is measured in milliseconds
Why is Latency important?
Low latency is very important for real time applications such as VoIP calls, video calling, financial trading platforms, Artificial intelligence video etc
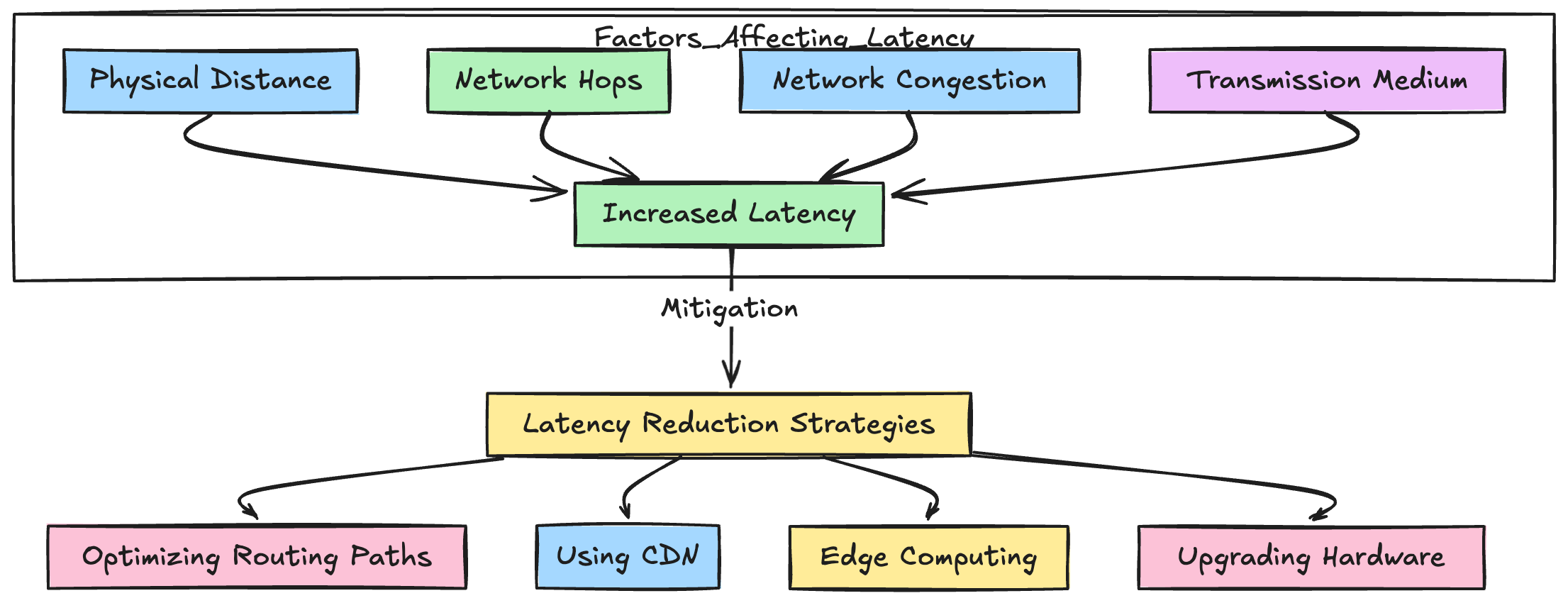
Factors affecting latency
- Physical Distance:
- The larger the distance between the source and the destination, the greater will be the latency .
- This is because more time will be required for the signal to go from the source to the destination.
- Network Hops:
- Each router or switch the data packet passes through increases the time required to reach its destination
- Network Congestion:
- Higher levels of network congestion creates hurdles and queues that data packet must traverse thus creating delay and causing increased latency
- Transmission Medium:
- Different mediums of transmission such as fibre optics or copper wire have different speeds and susceptible to varying degrees of interference
Reduction Strategies
- Optimizing Routing Paths:
- Configure the router paths such that there is least amount of congestion and fewer hops between the source and the destination of the data packets
- Using CDN to deliver the data packets faster:
- Use the CDN to cache the data at the edge that is nearer to the user and deliver the data to the user faster
- Edge Computing
- Here you process the data closer to the user in order to reduce geographical distance between the data source and delivery
- Upgrading data transmission hardware
- Upgrading the data transmission hardware to the hardware which is much more capable increases speed.
- Hardware includes upgrading from copper wire to fibre optics, using better and faster router and switches etc.
3 . Throughput
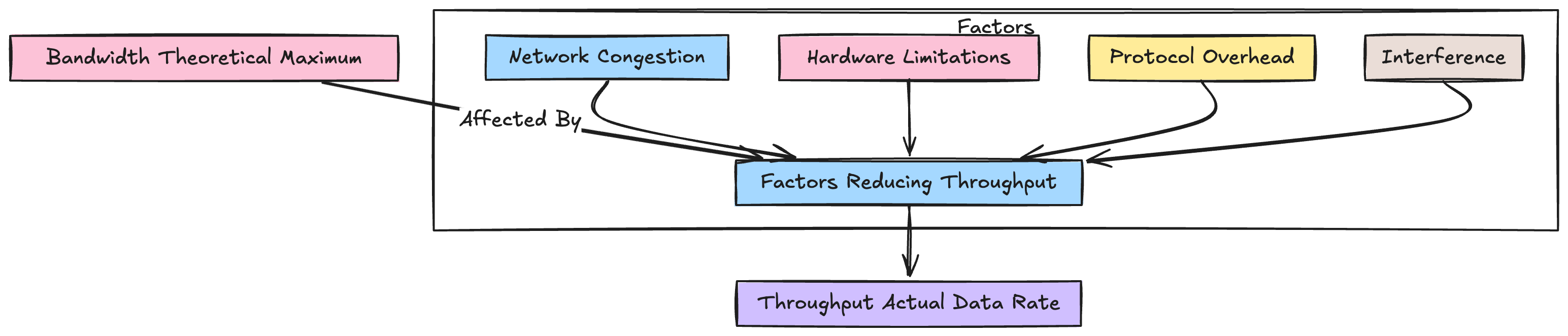
Throughput is the actual rate at which data can be successfully transferred across the network
When compared to the bandwidth which is the theoretical limit at which data can be transferred and which may or may not be achieved
Throughput is the real world data transmission capability that can be achieved and it is measured in Mbps
Why is Throughput Important
High Throughput means the network is capable in delivering large amount of data transfer without the bottlenecks, which is important for efficient utilization of network and bandwidth
Factors affecting throughput
- Network Congestion:
- High traffic can reduce throughput due to network congestion and packet loss and retransmissions
- Hardware limitations:
- Older hardware that have a lower limit of thoughput and bandwidth will limit the throughput
- Protocol overhead
- Many communication protocols also add extra overhead for control and security thus reducing the throughput that can be achieved
- Interference
- This is mostly true for wireless network but also can happen in wired networks. Interference reduces the amount of throughput that can achieved causing error and retransmission and blocking network paths.
Enhancement techniques
- Load Balancing:
- Load balance the traffic through different routes and servers to optimize network usage
- Traffic Prioritization
- prioritize important tasks such as web browsing and streaming and keep on low priority tasks such as backups
- Upgrading Hardware:
- Upgrade to latest hardware routers and switches along with better cabling to get the best throughput
- Using better protocols
- using protocols according to needs UDP is a protocol that provides better throughput as compared to TCP but lacks some features. Use the protocols according to use-case.
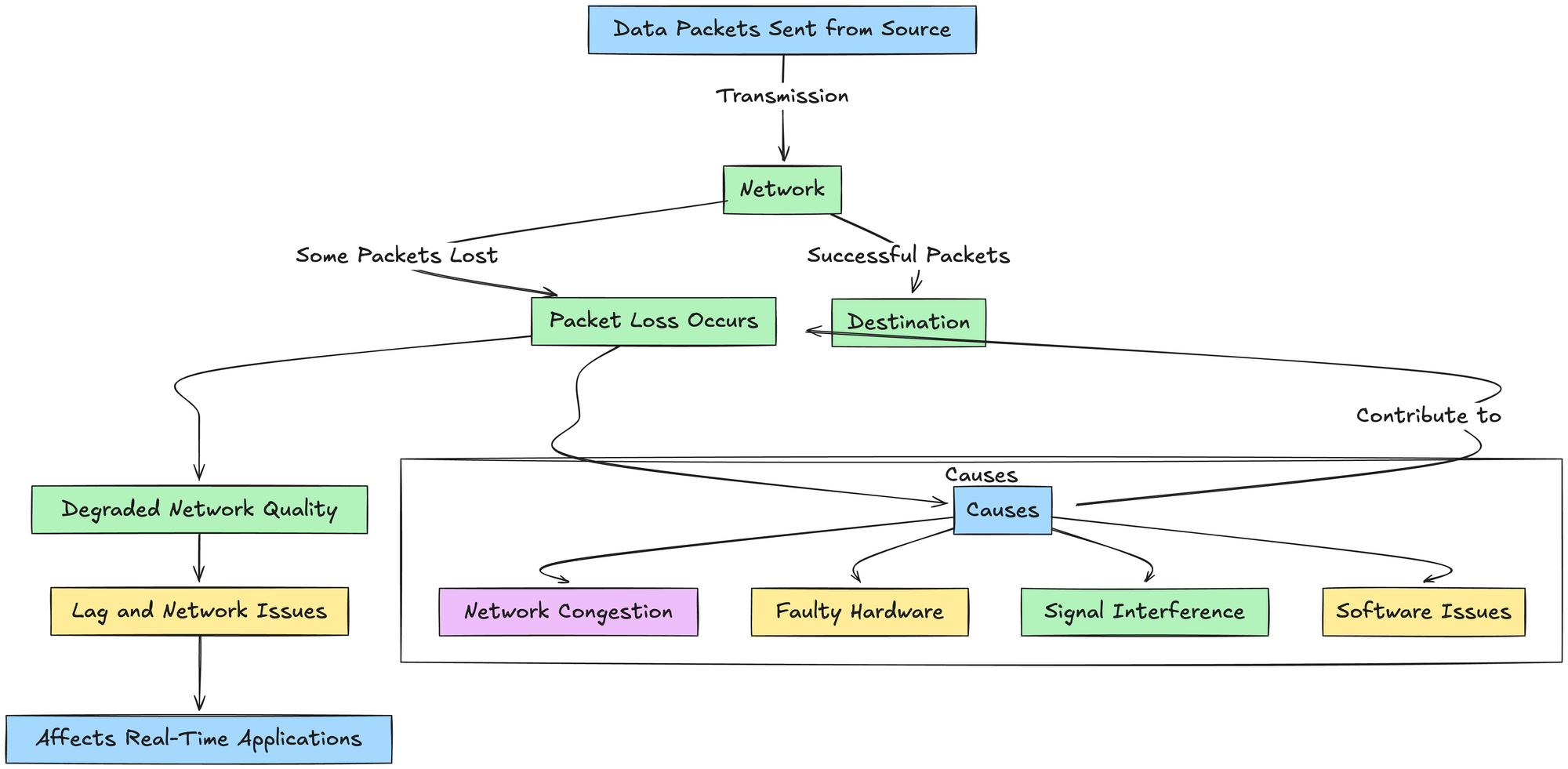
4. Packet loss
Packet loss is the percentage of data packets that are sent from the source but never reach the destination and are lost forever.
Why is Packet loss important?
Packet loss can degrade the network quality because the packets that are lost need to resent again this creates lag and all sorts of network issues
High packet loss can also result in broken or degraded quality of video and audio calling and affects the real time applications the most.
Packet loss affects all types of applications but it affects the real time applications the most.
Causes
- Network Congestion:
- Overloaded networks start to drop packets because they cannot handle any more packets.
- Faulty Hardware:
- Defective cables, routers and switches can cause packet loss, removing these faulty hardware with newer and modern networking equipment improves the packet delivery and reduces packet loss
- Signal Interference:
- Signal interference is a major problem in wireless networks but can also occur in wired connections as well. These could come from many factors such as other devices, electromagnetic fields etc
- Software issues:
- If the networks are not configured properly there could be bugs in the networking software and myraid or other problems can cause packet loss issues
- These problems must be studied with the help of tools and debugged in order to improve the packet loss
Mitigation strategies
- Network Redundancies
- Implementing multiple network paths and failover mechanism is a good way to ensure that there is always a path available for data packets to reach their destination best
- Error correction protocols
- If there is a situation where packet loss cannot be avoided using protocols such as TCP which has built in mechanism that requests retransmission of lost packets can be used to mitigate problems caused by packet loss
- Regular Maintenance:
- Performing routine checks on hardware and properly updating the software on networking devices can improve packet loss
- Improving Signal Quality
- In wireless networks using signal boosters and using newer generation of wireless technologies such as wifi 6 can improve the packet loss
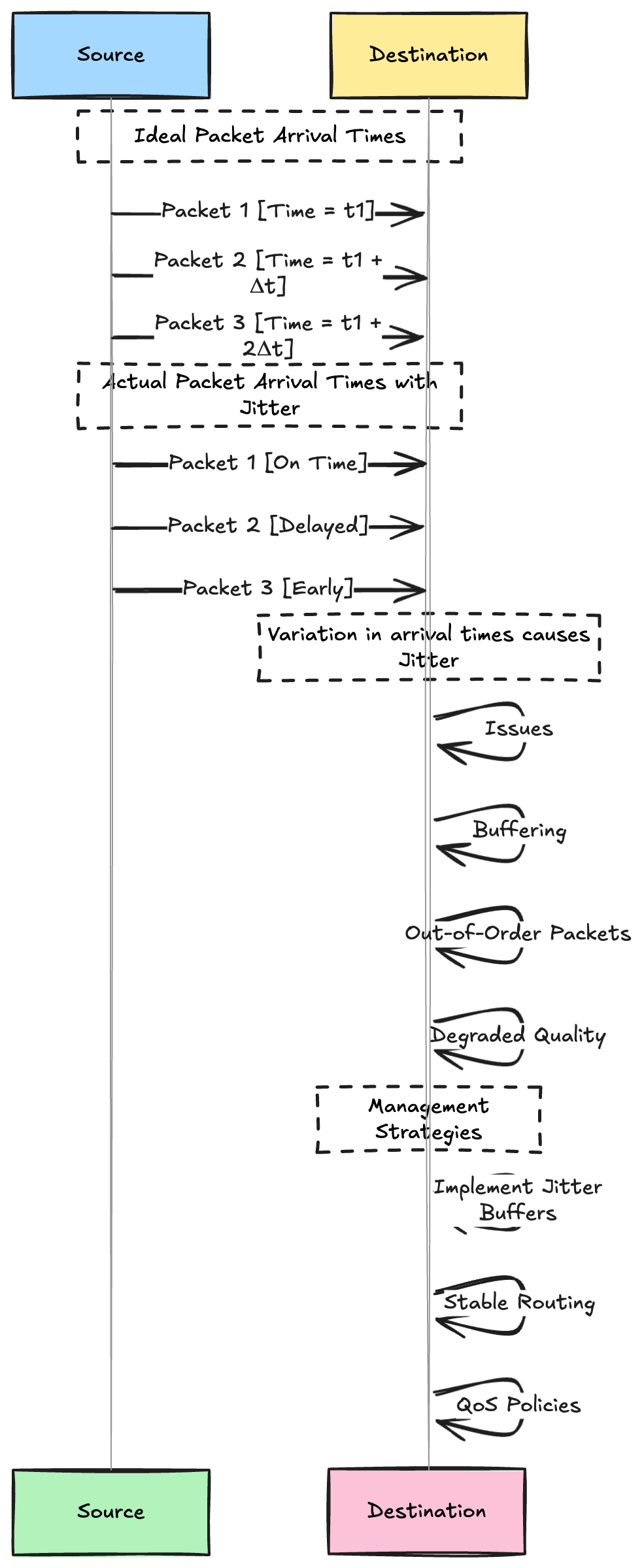
5. Jitter
Jitter is the variation in time, between the data packets arriving.
That is the difference in time between a data packet arriving and the time it takes for the next data packet to arrive
Thus it is the variability in latency of data packets.
Jitter is caused by a multitude of factors like network congestion, timing drift and route changes
Why is Jitter important?
Consistent delivery of data packets is important when streaming video or audio.
High Jitter can lead to buffering, out of order packets and degraded quality of service
Causes
- Network Congestion:
- Network congestion can happen due to high load of traffic and can cause network jitter.
- Buffer bloat:
- buffer bloat can happen when there is use of excessive buffer that leads to high latency and jitter
Management Strategies
- Implementing Jitter Buffers
- Jitter buffers temporarily store data packets in order to smoothen out the timing variations that is jitter before processing.
- Stable Routing:
- configure network to minimize routing changes and prefer a consistent network path
- QoS Policies:
- Prioritize the real time applications in order to reduce the jitter and make it smooth
- Monitoring and adjustment
- Monitor the jitter levels and make adjustments to the network so as to reduce the jitter
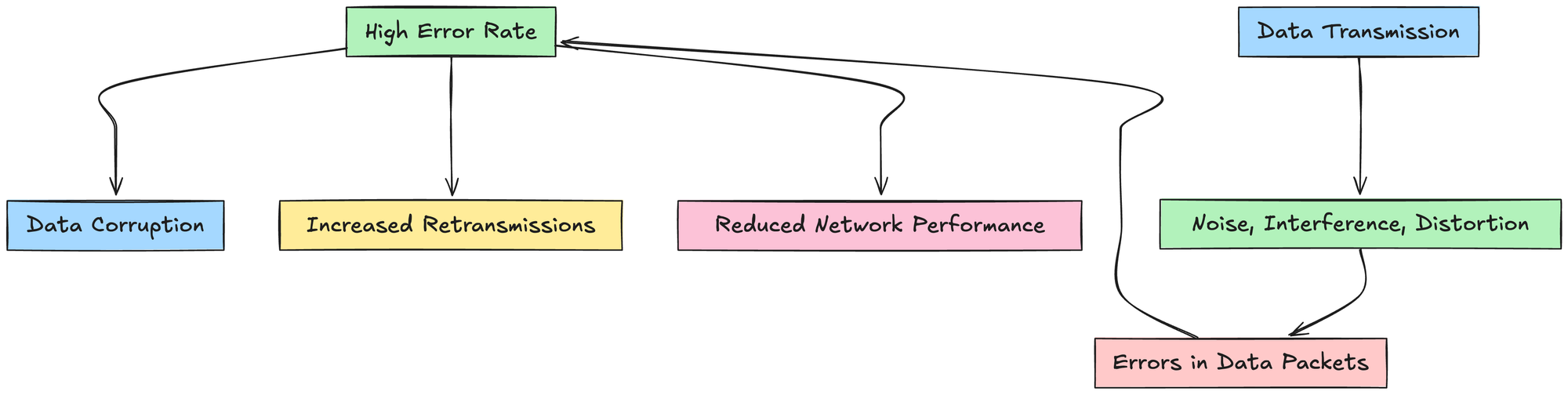
6. Error Rate
Error rate measures the frequency of error that are occurring in the data packets that are transmitted over a network.
Error rate is also called as the Bit Rate error, it indicates the number of bits that have been altered due to noise, interference, distortion or synchronization errors
Why is error rate important?
High rate of error can lead to data corruption , increased transmission and overall reduced network performance
reliable data transmission is important for apps that require data integrity
Monitoring techniques
- Cyclic redundancy check:
- This is method that is used to detect errors in digital data
- Parity checks:
- this is a simple method to check error by detecting the number of set bits is even or odd
- error logs:
- Network devices often maintain logs error that you can read and analyze why that is happening
Reduction strategies
- Hardware maintenance:
- Regularly maintaining the hardware reduces the error rate and maintains the performance of the equipment
- Signal boosting:
- Especially in wireless network you can use the Signal boosting to increase the signal quality and reduce the error rate
- Shielded cabling
- Shielding the cabling reduces the electromagnetic fields and interference
- Environmental controls
- Ensuring good working conditions like temperature and humidity makes the hardware equipment work
Metered TURN Server
- API: TURN server management with powerful API. You can do things like Add/ Remove credentials via the API, Retrieve Per User / Credentials and User metrics via the API, Enable/ Disable credentials via the API, Retrive Usage data by date via the API.
- Global Geo-Location targeting: Automatically directs traffic to the nearest servers, for lowest possible latency and highest quality performance. less than 50 ms latency anywhere around the world
- Servers in all the Regions of the world: Toronto, Miami, San Francisco, Amsterdam, London, Frankfurt, Bangalore, Singapore,Sydney, Seoul, Dallas, New York
- Low Latency: less than 50 ms latency, anywhere across the world.
- Cost-Effective: pay-as-you-go pricing with bandwidth and volume discounts available.
- Easy Administration: Get usage logs, emails when accounts reach threshold limits, billing records and email and phone support.
- Standards Compliant: Conforms to RFCs 5389, 5769, 5780, 5766, 6062, 6156, 5245, 5768, 6336, 6544, 5928 over UDP, TCP, TLS, and DTLS.
- Multi‑Tenancy: Create multiple credentials and separate the usage by customer, or different apps. Get Usage logs, billing records and threshold alerts.
- Enterprise Reliability: 99.999% Uptime with SLA.
- Enterprise Scale: With no limit on concurrent traffic or total traffic. Metered TURN Servers provide Enterprise Scalability
- 5 GB/mo Free: Get 5 GB every month free TURN server usage with the Free Plan
- Runs on port 80 and 443
- Support TURNS + SSL to allow connections through deep packet inspection firewalls.
- Supports both TCP and UDP
- Free Unlimited STUN