Latency in networking is the time it takes for a packet of data to travel from its source to destination.
This time is typically measured in milliseconds as the data travels at the speed of light, but variety of factors influence the time required to travel
These factors include the
- The phycical distance between devices
- the quality of network connection, this include factors like jitter, the connection is fiber ir over wifi etc. If the quality of the netwok is better then the latency is lower
- the number of routers, swithces that are between the devices. If there are more devices then there is greater latency
- the traffic congestion is another factor, there is there is a lot of congestion then there is more latency
Latency Vs Bandwidth
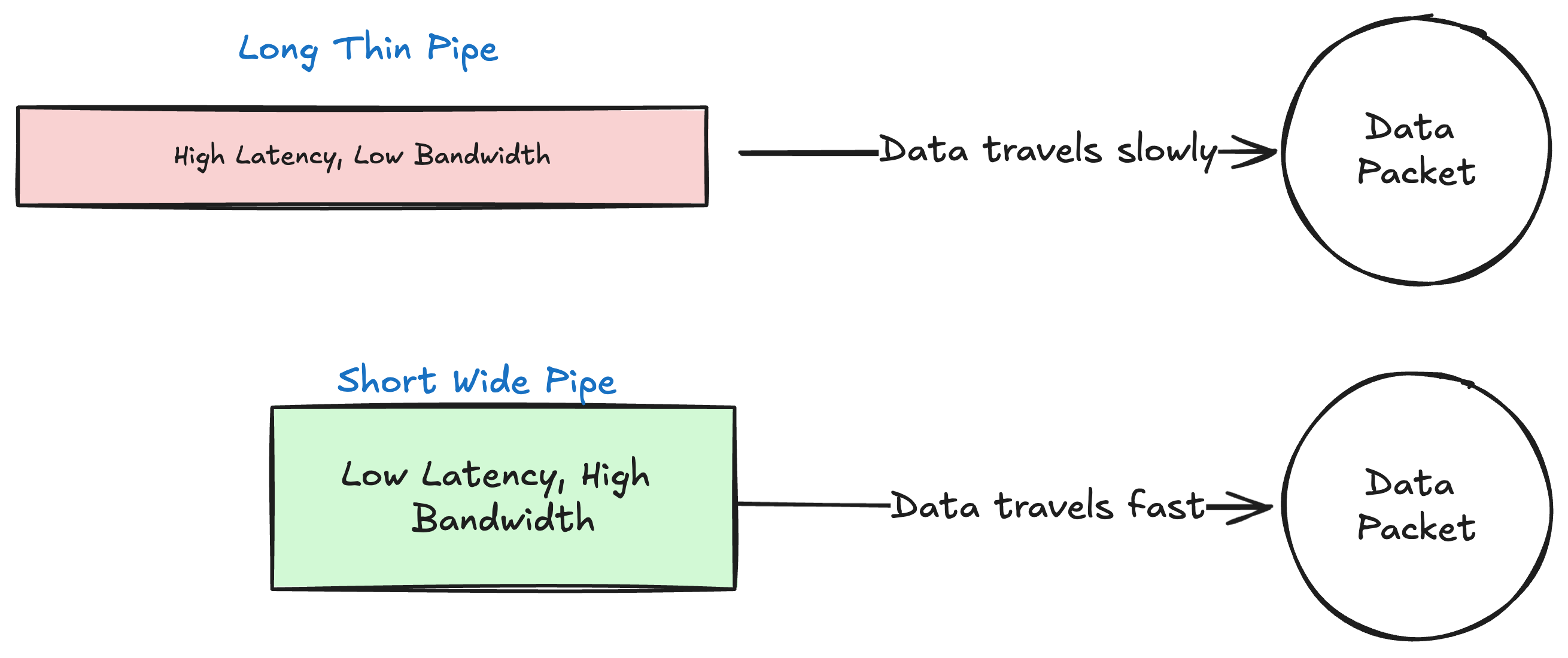
Latency is a the time delay in sending a packet of data from one point to another
bandwidth is the maximum rate at which data can be transferred from one point to another in a network over a specific period of time. Bandwidth is measured in bits per seconds
Think of it as a pipe transferring data from one point to another, bigger the bandwidth means bigger the diameter of the pipe, hence more data can travel.
Latency on the other hand is the time delay in a packet of data reaching its destination. think of it like, how long is the pipe and hence how long the data needs to travel, are there any leaks in the pipe, are the valve and regulators in the pipe and how many are there
Even a pipe with a large diameter (high bandwidth) there can be delays in a data reaching its destination because of distance, congestion, leaks, valves and regulators ( High Latency) and such that.
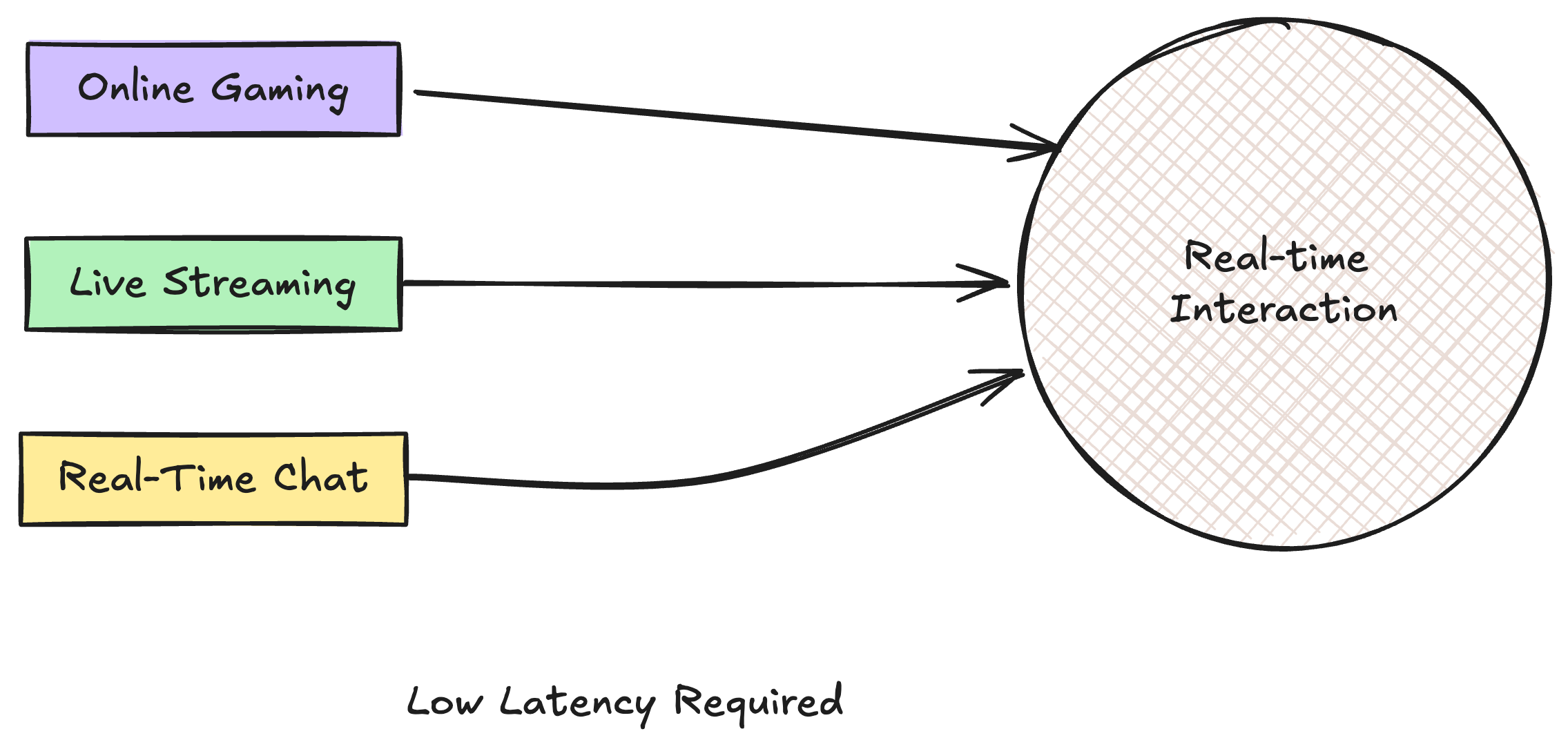
Why Low Latency is Important for performance
Low latency is important for performance in many applications, this is most important in applications that require real time communications like notifications and real time chat etc
- Real Time Applications: Real time apps such as real time chat, online gaming and gaming platforms like strada survive only thorough low latency, ultra low latency live streaming for sports etc require req and response feedback cycle which is only achievable with low latency
- Enhanced Responsiveness: Low latency results in highly responsive applications, the apps even through run through the internet but it feels as if they are running natively thanks to low latency networks
- Efficiency in Automated Systems: If you have automated systems like for example automatic trading bots that trade based on signals in the market, these systems need ultra low latency because markets are moving and these systems need to make decisions in real time.
Impact of Latency on User Experience and Operational Efficiency
- User Experience (UX): High latency can badly impact user experience, expecially in instances where the nature of the app is real time. For example if someone is
- Operational efficiency: In business latency can affect the efficiency of the operational processes that depend on timely data
- Quality of service: Quality of service degrades due to latency issues, this is important in software business that provide api and sdk services to other business and hence the quality of service of software businesses is dependent of low latency
How can you measure Latency?
Ping
The most common tool for measuring latency is ping command. This command line utility sends a ICMP echo request to the target host and listens for replies
The time taken for these packets to travel to the host and back is called as round-trip time, this helps in assessing network stability and consistency in latency.
Traceroute
The tranceroute is a utility that tracks a path that a packet of data travels through form the source device to the destinations
In the path the packet encounters many devices such as routers and switches, it provides the list of routers and the time to reach that devices when it passes it
This tools can be used to diagnose where latency is occouring in the path of the packet from the device to the destination.
Network performance monitoring tools
there are specific tools that can be used to monitor networking performance, these include contineous monitoring and alert administration when network performance deviates from the performance metrics
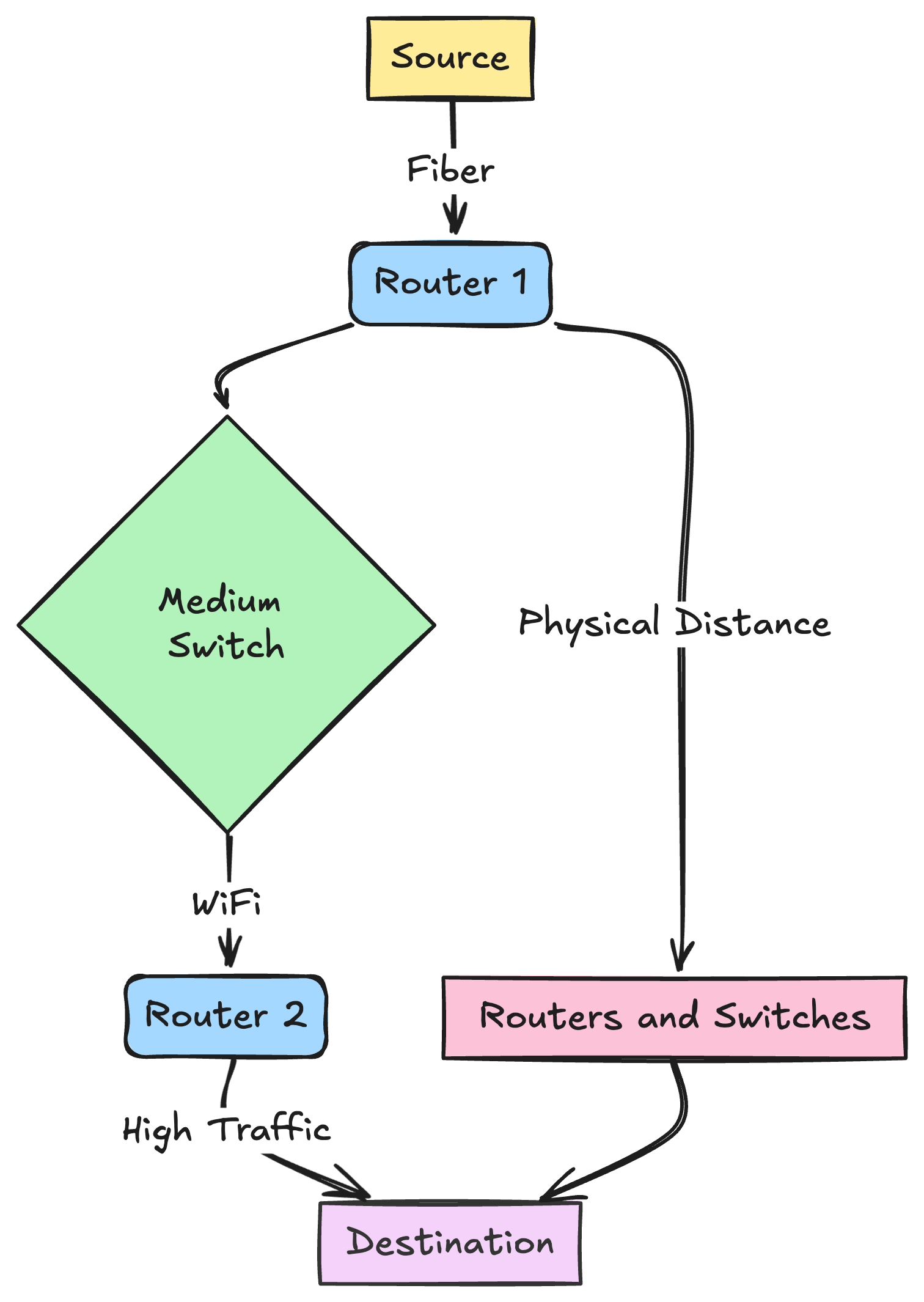
What are the causes of latency?
Here are some of the majot causes of latency:
Propagation Delay:
This is a primary factor and this refers to the time it takes for the packet of data to travel from one place to another through a medium of travel such as fiber or wifi.
The fastest the packet travels is close to the speed to light, but phycical distance and the type of medium such as wifi is slower than fiber are significant factors
Transmission Medium:
The type of medium through which the data is travels also plays a factor in determining the speed of travel and hence the latency
the fastest medium is the fiber optic cable, other mediums are slower and include copper wire, wifi radios etc.
Router and Switch Processing Time
Routers and switches that are in the path of the data also plays a role, any additional router or switch in the path increases latency that is due to additional processing and directing the data to the next hop. The more hops are there between the source device and the destination device the higher the latency
Traffic Load
High traffic load leads to more latency and the medium of travel gets crowded and then packets of data gets queued to be processesed and transmittedf
congestion leads to traffic bottlenecks much like congestion in traffic on highways leads to traffic bottlenecks
Network Protocols
Different Protocols require different amount of processing time. What type of network protocol you are using to transmit the data also affects the latency
Server Processing Time
How fast the server processes the request and responds to the request also affects the latency of the data
Quality of Service (QoS) settings
If there are some quality of service settings done on the router than this could also affect the latency. As some services will have priority in processing and other have a lower priority. the service with a lower priority might experience greater latency as the data packets might have to wait in a queue to be processed and then transmitted
Metered TURN servers
- API: TURN server management with powerful API. You can do things like Add/ Remove credentials via the API, Retrieve Per User / Credentials and User metrics via the API, Enable/ Disable credentials via the API, Retrive Usage data by date via the API.
- Global Geo-Location targeting: Automatically directs traffic to the nearest servers, for lowest possible latency and highest quality performance. less than 50 ms latency anywhere around the world
- Servers in all the Regions of the world: Toronto, Miami, San Francisco, Amsterdam, London, Frankfurt, Bangalore, Singapore,Sydney, Seoul, Dallas, New York
- Low Latency: less than 50 ms latency, anywhere across the world.
- Cost-Effective: pay-as-you-go pricing with bandwidth and volume discounts available.
- Easy Administration: Get usage logs, emails when accounts reach threshold limits, billing records and email and phone support.
- Standards Compliant: Conforms to RFCs 5389, 5769, 5780, 5766, 6062, 6156, 5245, 5768, 6336, 6544, 5928 over UDP, TCP, TLS, and DTLS.
- Multi‑Tenancy: Create multiple credentials and separate the usage by customer, or different apps. Get Usage logs, billing records and threshold alerts.
- Enterprise Reliability: 99.999% Uptime with SLA.
- Enterprise Scale: With no limit on concurrent traffic or total traffic. Metered TURN Servers provide Enterprise Scalability
- 5 GB/mo Free: Get 5 GB every month free TURN server usage with the Free Plan
- Runs on port 80 and 443
- Support TURNS + SSL to allow connections through deep packet inspection firewalls.
- Support STUN
- Supports both TCP and UDP
- Free Unlimited STUN
What are the factors other than latency that determine network performance
- Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted from one point to another in a network in a specified amount of time
This is usually measured in megabits per second
The more bandwidth there is the more high volume applications like video streaming can work or large file transfer can take place
- Throughput
Throughput is the actual data transfer that is achieved. It is often lower than the bandwidth due to various factors like network congestion and hardware limitations
Throughput is the actual measure of how much data transfer is actually achieved in a given time frame that directly affects application performance and user experience
- Jitter
Jitter is the variability in time frame between packets arrive at a destination. Jitter is caused due to network congestion and various other factors
Jitter can cause poor performance in real time applications such as video streaming and VoIP or video calling apps
To learn more about Jitter you can refer to this article: What is Jitter? Common Causes and how to reduce internet Jitter
- Packet Loss
Packet loss occurs when one or more data packets start from a source and fail to reach their destination.
This can happen due to errors in data transmission network congestion, faulty hardware, bad network quality etc
Packet loss can severely affect network performance and reliability leading to distruptions in application performance and the need for data to be retransmitted again and again.
- Error Rate:
The Error rate measures the number of corrupted bits as a ratio of total bits sent.
The bits can be corrupted due to electromagnetic interference, physical damage to cables and other transmission issues
A high error rate necessitates retransmissions that can slow down throughput and increase the latency in the network and degrades the network performance
- Network Reliability:
Network reliability refers to a network ability to perform its functions under set conditions for a specific amount of time
like for example 99% reliability means that the network can performs its duties 99 % of the time
reliable networks have less downtime and provides stable services and connections
- Quality of Service:
Quality of service are a set of rules that manage network resources by setting priorities of which types of services get access to internet first
This ensures that important services and critical applications have access to more bandwidth and resources on a priority then less critical services
for example video calling and real time applications would get preference over web browsing
- Network Congestion:
Network congestion occours when there is too much traffic or data on a network, that is more than a network can carry, this degrades the network quality
Network congestion can lead to packet loss increased latency and jitter thus affecting the data transmission in a network
- Scalability:
Scalability refers to the ability of a network to handle growing amount of traffic including more network throughput and multiple devices that are connected to the network
A scalable network can maintain performace levels even during peak times when there are multiple devices connected to the network that are using high bandwidth applications such as video calling and internet work and presentations
How can you improve network latency issues?
Upgrade Network Infrastructure:
Always use high quality networking hardware, like optical fiber and good quality routers etc can help reduce latency issues
Minimize physical distance
Always try to minimize the physical distance between devices, you can connect to devices that are closer to each other without much latency
Optimize network design and configuration
Network design also plays an important role in latency. Designing a good network where data does not have to travel between hops to reach other devices helps in reducing latency
Utilize modern Network Protocols
Use modern networking protocols like UDP and accelerated TCP protocols for faster transmission of data.
Reduce Network load
Reduce unnecessary data transfer so as to reduce the load on the network. having a lot of traffic in the network creates network congestion which in turn increases latency
Regularly Monitor and optimize Network
Always keep a check and regularly monitor network activity to see if there are any problems with the network which can be improved and the speed restored
Improve software efficiency
Write better software on the server and also on the client that sends data as needed which improves latency and reduces load times
Thus we have learned in this article what is low latency, and how we can improve latency for better response time and better experience in content consumptionone as well as in business.
Here are some of our other articles
